Activity 4.1/5.1 how can you identify organic macromolecules – Activity 4.1/5.1: Identifying Organic Macromolecules introduces the fundamental principles and techniques for characterizing and identifying these complex biomolecules. Understanding the structure and composition of organic macromolecules is crucial for comprehending various biological processes and their implications in medicine, biotechnology, and other scientific fields.
This exploration delves into the unique characteristics of organic macromolecules, such as their high molecular weight, complex structure, and biological significance. It provides a comprehensive overview of the methods employed to identify these molecules, including chemical tests, spectroscopic techniques, chromatographic techniques, and mass spectrometry.
1. Organic Macromolecules: Activity 4.1/5.1 How Can You Identify Organic Macromolecules
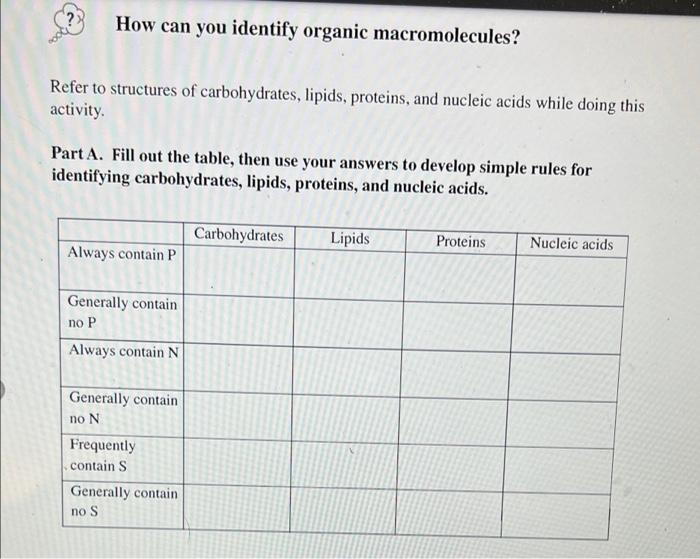
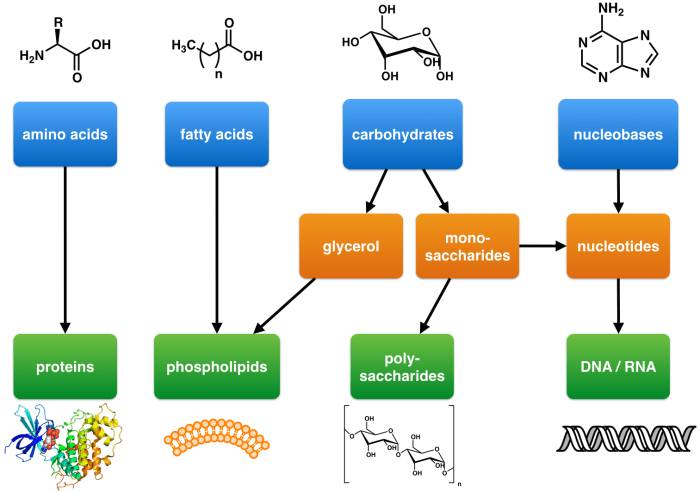
Organic macromolecules are large, complex molecules that are essential for life. They are made up of repeating units called monomers, which are linked together by covalent bonds. Organic macromolecules can be classified into four main types: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Organic macromolecules are important because they provide the building blocks for cells and tissues, and they play a vital role in many biological processes. For example, carbohydrates provide energy, proteins are involved in cell structure and function, lipids form cell membranes, and nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information.
Examples of Organic Macromolecules
- Carbohydrates: glucose, starch, cellulose
- Proteins: enzymes, hormones, antibodies
- Lipids: fats, oils, waxes
- Nucleic acids: DNA, RNA
2. Identifying Organic Macromolecules
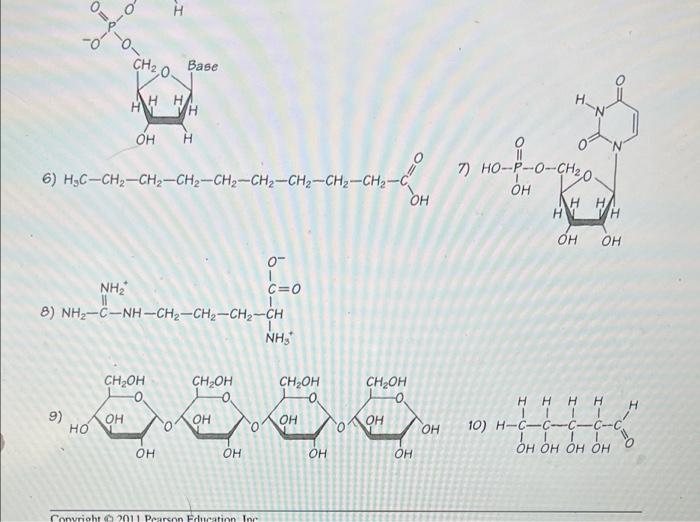
Characteristics of Organic Macromolecules
- Large molecular size
- Complex structure
- Contain carbon atoms
- Covalent bonding
- Polar or nonpolar
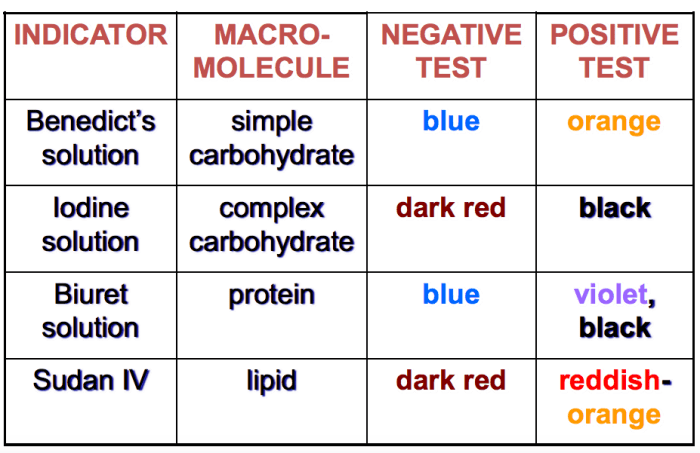
Chemical Tests for Identifying Organic Macromolecules
Chemical tests can be used to identify organic macromolecules based on their specific chemical properties. Some common chemical tests include:
- Benedict’s test: detects reducing sugars (carbohydrates)
- Biuret test: detects proteins
- Sudan III test: detects lipids
- Orcinol test: detects pentose sugars
3. Spectroscopic Techniques
Spectroscopic techniques can be used to identify organic macromolecules based on their absorption or emission of electromagnetic radiation. Some common spectroscopic techniques include:
- Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy
- Infrared (IR) spectroscopy
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy
- Mass spectrometry
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spectroscopic Techniques
Spectroscopic techniques offer several advantages for identifying organic macromolecules, including their high sensitivity, specificity, and ability to provide detailed structural information. However, they can also be expensive and time-consuming.
4. Chromatographic Techniques
Chromatographic techniques can be used to separate and identify organic macromolecules based on their different physical and chemical properties. Some common chromatographic techniques include:
- Paper chromatography
- Thin-layer chromatography (TLC)
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- Gas chromatography (GC)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Chromatographic Techniques, Activity 4.1/5.1 how can you identify organic macromolecules
Chromatographic techniques offer several advantages for identifying organic macromolecules, including their ability to separate complex mixtures, their high sensitivity, and their relatively low cost. However, they can also be time-consuming and require specialized equipment.
5. Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that can be used to identify organic macromolecules based on their mass-to-charge ratio. Some common mass spectrometry techniques include:
- Electron ionization mass spectrometry (EI-MS)
- Chemical ionization mass spectrometry (CI-MS)
- Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS)
- Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry offers several advantages for identifying organic macromolecules, including its high sensitivity, specificity, and ability to provide detailed structural information. However, it can also be expensive and time-consuming.
Key Questions Answered
What are the key characteristics of organic macromolecules?
Organic macromolecules are typically high molecular weight, composed of repeating subunits, and exhibit complex structures with specific biological functions.
How can chemical tests be used to identify organic macromolecules?
Chemical tests, such as the Biuret test for proteins and the Molisch test for carbohydrates, provide qualitative information about the presence of specific functional groups within organic macromolecules.
What are the advantages of using spectroscopic techniques to identify organic macromolecules?
Spectroscopic techniques, such as UV-Vis spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy, allow for the identification of organic macromolecules based on their absorption or emission of electromagnetic radiation at specific wavelengths.
How does mass spectrometry contribute to the identification of organic macromolecules?
Mass spectrometry determines the molecular weight and structure of organic macromolecules by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of their constituent ions.