All the following are events of early inflammation except for a select few. Early inflammation, a complex biological response, involves a cascade of events that set the stage for tissue repair and healing. Understanding the exclusions from this process is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of inflammatory conditions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the mechanisms and significance of events that are not part of early inflammation, providing a clear distinction between the initial and subsequent phases of the inflammatory response.
Early Inflammation
Early inflammation is the initial phase of the inflammatory response, characterized by a rapid influx of neutrophils and other immune cells to the site of injury or infection. This process is mediated by a variety of chemical mediators, including cytokines, chemokines, and lipid mediators.
Events of Early Inflammation, All the following are events of early inflammation except
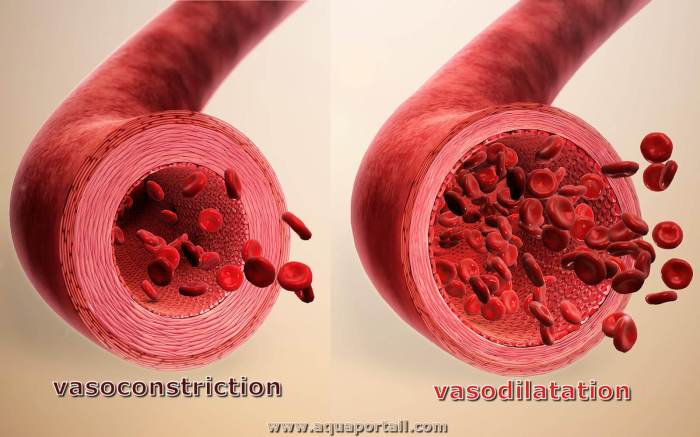
- Vasoconstriction
- Increased vascular permeability
- Neutrophil adhesion and migration
- Phagocytosis of pathogens
- Release of inflammatory mediators
These events are essential for the recruitment and activation of immune cells to the site of inflammation and for the clearance of pathogens.
Exclusions from Early Inflammation
Events that are not part of early inflammation include:
- Lymphocyte infiltration
- Macrophage activation
- Tissue repair
These events are typically associated with late inflammation, which occurs after the initial influx of neutrophils.
Comparison of Early and Late Inflammation
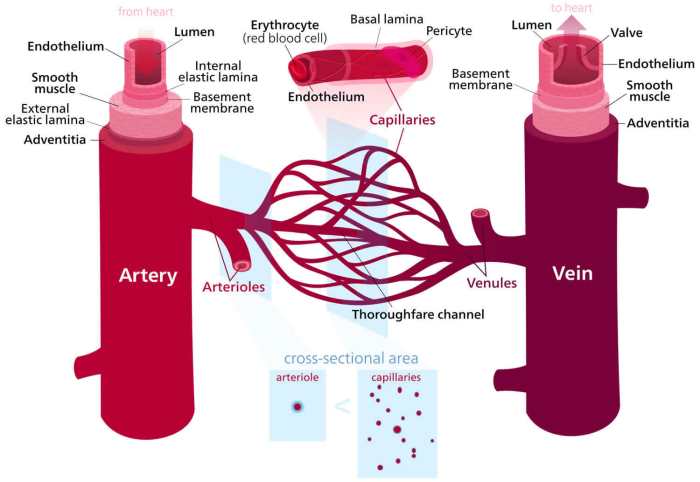
| Event | Mechanism | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Early inflammation | Neutrophil infiltration, release of inflammatory mediators | Hours to days |
| Late inflammation | Lymphocyte infiltration, macrophage activation, tissue repair | Days to weeks |
Clinical Implications
Understanding early inflammation is important for the diagnosis and treatment of a variety of diseases, including sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and inflammatory bowel disease. Early inflammation can be detected by measuring the levels of inflammatory mediators in the blood or by imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scanning.
Treatment of early inflammation typically involves the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These drugs can help to reduce the symptoms of inflammation and prevent tissue damage.
Future Directions
There are a number of areas of future research on early inflammation. These include:
- Identifying new inflammatory mediators
- Developing new drugs to target early inflammation
- Understanding the role of early inflammation in the development of chronic diseases
These studies will help to improve our understanding of early inflammation and its role in disease, and may lead to new treatments for a variety of inflammatory conditions.
FAQ: All The Following Are Events Of Early Inflammation Except
What are the key differences between early and late inflammation?
Early inflammation is characterized by neutrophil infiltration, vasodilation, and increased vascular permeability, while late inflammation involves monocyte/macrophage infiltration, tissue remodeling, and angiogenesis.
Why is it important to exclude certain events from the definition of early inflammation?
Excluding events that occur after the initial response helps define the specific mechanisms and mediators involved in the early stages of inflammation, enabling targeted therapeutic interventions.
How can understanding early inflammation improve clinical practice?
By identifying and targeting events specific to early inflammation, clinicians can develop more effective treatments for inflammatory diseases, potentially preventing chronic complications and improving patient outcomes.